All-in-one platform for
We have combined cutting-edge AI-technology with powerful tools to streamline business operations, enabling smarter decisions and greater efficiency.
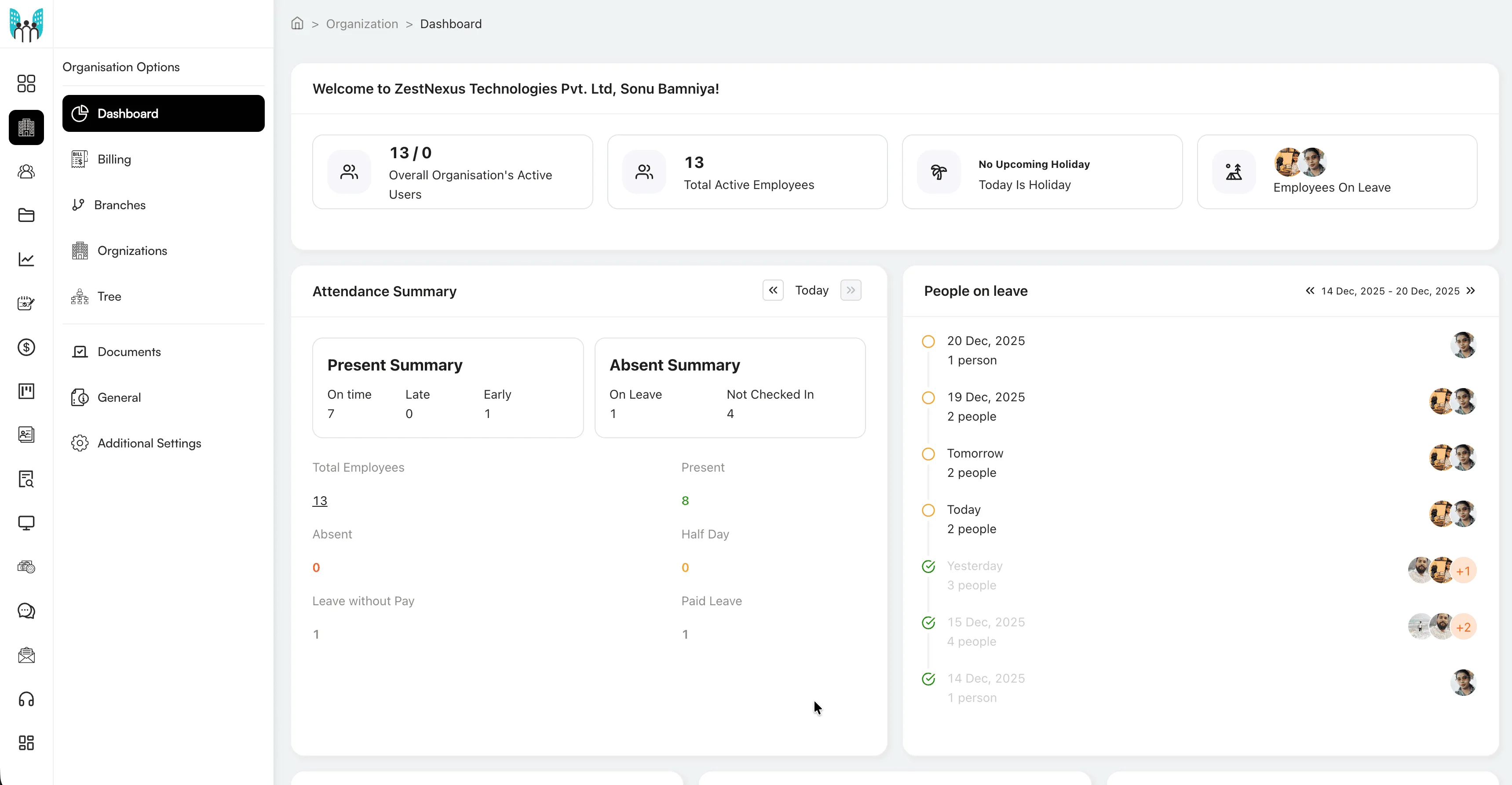
We have combined cutting-edge AI-technology with powerful tools to streamline business operations, enabling smarter decisions and greater efficiency.

We have combined cutting-edge AI-technology with powerful tools to streamline business operations, enabling smarter decisions and greater efficiency.
Comprehensive Employee Management System designed to streamline and simplify your HR processes.
Run Payroll in 2 simple steps: Generate Payroll and Verify and confirm.
AI-powered tool simplifies task tracking, resource allocation, and collaboration for productive teams.
Powerful Time Tracking App that allows you to monitor employee work hours with accuracy and flexibility.
Robust attendance management system with geofencing that integrates seamlessly with various work patterns.
Advanced security features with AI-powered insights to protect your business data and operations.
ZestNexus is trusted by over 100 organizations worldwide to streamline their HR and business operations, delivering proven results and driving efficiency across teams.
From HR and Payroll to Project and Lead Management, ZestNexus offers a complete suite of tools to streamline your operations in one unified solution.
Organizations Trust Us
Client Support & Customization
ZestNexus HRMS has completely transformed the way we manage our HR operations. From Onboarding to Payroll, Attendance Tracking to Performance Management, every aspect is seamlessly integrated into One Intuitive Platform. The User Interface is Clean and Easy to Navigate.
Shivam Dwivedi, HR Manager
Here's what our customers have to say about their experience with ZestNexus. These testimonials highlight the impact our platform has had in transforming their business operations and driving efficiency across teams.
As a plywood showroom owner our work is not limited to showroom. Our team has to continuously move, deliver orders and fix our customer problems. Earlier it was a big challenge. But as soon as we started using ZestNexus software, everything becomes so much easier and well synchronised.
ZestNexus HRMS has completely transformed the way we manage our HR operations. From Onboarding to Payroll, Attendance Tracking to Performance Management, every aspect is seamlessly integrated into One Intuitive Platform. The User Interface is Clean and Easy to Navigate.
ZestNexus has transformed our operations at Anaya Pathology, streamlining money management and simplifying referral tracking. Its detailed report feature provide valuable insights into growth, helping us address bottlenecks quickly.
Dealing in hardware business means multiple shifts, working on site and changing schedules. And to keep track of all of it manually was a headache for our HR. But thanks to ZestNexus, as it has made our entire work process smoother and easier.
As a real estate company me and my team are always on the move. From site visits to client meetings, negotiations to final pricing everything was keeping us stuck. However, for the last month we have been using ZestNexus, and I must say everything is feeling effortless now.
ZestNexus has proven to be a true game changer for us. I will definitely recommend this software to all business types. Now we are saving a lot of time and it has become way too easy to keep everything in order without stress.
Connect seamlessly with popular platforms and services to enhance your workflow.
Start NowZestNexus offers a powerful suite of tools to streamline your HR processes, empowering your workforce and driving organizational success.
Explore this section to learn more about ZestNexus and find answers to your questions.
Can't find what you're looking for? Contact our customer support team
Join 100+ organizations already using ZestNexus to manage their operations more efficiently.